Sustainability DisclosureInformation Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
The MORESCO Group considers the impact of climate change on its business and vice versa to be one of its important management issues. The Group has established its "MORESCO Group Sustainability Policy" and regards itself as a specialist in the boundary areas as defined in its management philosophy. We will actively promote sustainability initiatives in order to be better trusted by our stakeholders through business operations while both "realization of a sustainable society" and "enhancing corporate value the in the medium-to-long term". We will also make further contributions to solving social and environmental issues. As part of this, the Group expressed its endorsement of the recommendations from the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and strengthened its climate change initiatives and information disclosure. Going forward, we will continue to enhance information disclosure in line with the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), respond to risks and opportunities such as climate change appropriately and in a timely manner, and aim to realize a sustainable society and promote corporate value in the medium-to-long term.

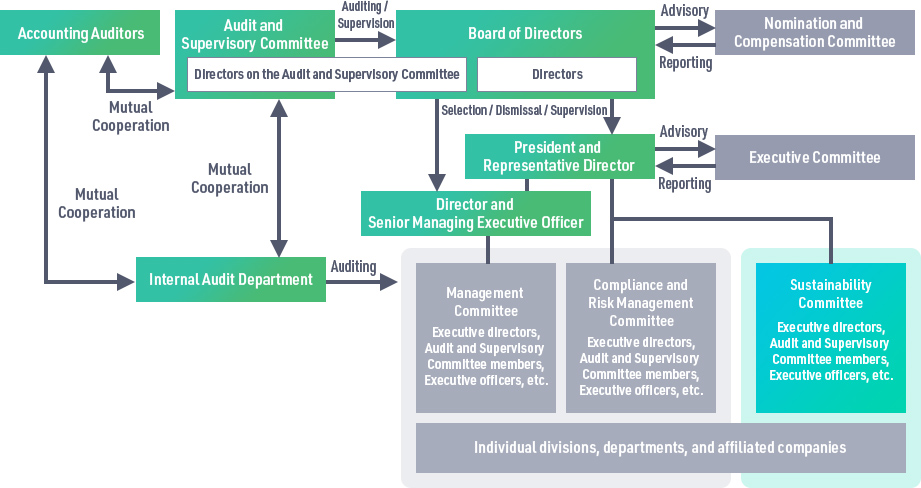
Ⅰ. Governance
In order to operate its business based on both the principles of "realization
of a sustainable society" and "enhancing corporate value the in the medium-to-long term", the Group
formed a "Sustainability Committee" in April 2022. In addition, we have also established the "Corporate
Sustainability Department", a dedicated department to oversee the Group's sustainability promotion
activities. Chaired by the President and Representative Director, The Sustainability Committee consists
of executive directors, the full-time audit and supervisory committee member, executive officers, and
other members. The committee meets once every six months to discuss a wide range of risks and
opportunities, including climate change and other social and environmental issues related to
sustainability, and reflects them in business strategies and policies in a timely manner.
The Board of Directors deliberates and makes decisions on business strategies, investment plans, BCPs,
etc. from the perspective of comprehensive compliance and risk management, following the Basic
Sustainable Policy and relevant material issues including climate change.
Ⅱ. Strategy (Risk and Opportunity Analysis)
The Group manufactures and sells chemical and petroleum products to be used as raw materials and fuels (including fossil fuels), and recognizes that climate change is an extremely important issue that brings both risks and opportunities.
1. Major climate-change-related risks and opportunities MORESCO faces (scenario analysis)
Regarding climate change, various scenarios can be considered depending on trends in global warming countermeasures taken by major countries. Assuming two typical scenarios, (1) Transition Risk Scenario (1.5°C or lower scenario) and (2) Physical Risk Scenario (4.0°C scenario), the Group examined risks and opportunities for our core businesses including specialty lubricants, raw materials, hot melts, and other new businesses, primarily for the period until the 2030s.
(1) Transition Risk Scenario (1.5°C or lower scenario)
- Prescriptive scenarios for achieving zero greenhouse gas emissions at a global scale by 2050
- In principle, policies, energy and industrial structure, resource prices, etc. are based on the "NZE2050 -Scenario" defined in the IEA's "World Energy Outlook 2023", and average temperature and other assumptions related to climate change are based on the "SSP1-1.9 Scenario" defined in the "IPCC Sixth Assessment Report".
(2) Physical Risk Scenario (4.0°C scenario)
- Scenario in which effective policies to address climate change issues are not implemented, incorporating the withdrawal of currently announced policies and targets for greenhouse gas reduction.
- In principle, policies, energy and industrial structure, resource prices, etc. are based on the "STEPS Scenario" defined in the IEA "World Energy Outlook 2023", and average temperature and other assumptions related to climate change are based on the "SSP5-8.5 Scenario" defined in the "The Sixth IPCC Assessment Report".
In identifying and selecting risks and opportunities, the Corporate Sustainability Department took
the lead in conducting study sessions at each business division based on the results of awareness
surveys conducted at major business divisions and making decisions based on the opinions of external
experts.
The main conclusions of the study are as follows.
risk
| Expected Events | Expected Time to Become Evident |
Material Risks | Countermeasures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5℃ Scenario |
Rising carbon prices | Medium term |
|
|
| Soaring raw material and fuel prices and procurement difficulties | Short-to-medium term |
|
|
|
| Changes in the competitive environment | Short-to-medium term |
|
|
|
| Changes in customer behavior | Short term |
|
|
|
| Responding to the circular economy | Short-to-medium term |
|
|
|
| Changes in Investors' and Financial Institutions' Awareness | Short term |
|
|
|
| 4.0℃ Scenario |
Rising average temperature | Short-to-long term |
|
|
| Intensification of extreme weather | Short-to-long term |
|
|
|
| Rising Sea level | Short-to-long term |
|
|
|
| Water Resources, Resource Recycling, Wastewater and Waste Management |
Short-to-medium term |
|
|
opportunity
| Expected Events | Expected Time to Become Evident |
Material Opportunities | Countermeasures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5℃ Scenario |
Rising carbon prices | Midium term |
|
|
| Soaring raw material and fuel prices and procurement difficulties | Short-to-medium term |
|
|
|
| Changes in the competitive environment | Short-to-medium term |
|
|
|
| Changes in customer behavior | Short term |
|
|
|
| Responding to the circular economy | Short-to-medium term |
|
|
|
| Changes in Investors' and Financial Institutions' Awareness | Short term |
|
|
|
| 4.0℃ Scenario |
Average temperature rise | Short-to-long term |
|
|
| Intensifyiing extreme weathers | Short-to-long term |
|
|
|
| Rising Sea level | Short-to-long term |
|
|
|
| Water Resources, Resource Recycling, Wastewater and Waste Management |
Short-to-medium term |
|
|
2. Financial impact
Financial implications of the Transition Risk Scenario
In the Transition Risk Scenario, the financial impact is expected to be particularly significant in the upstream supply chain due to rising base oil purchase prices caused by factors such as carbon pricing (introduction of a carbon tax). Under certain assumptions, our base oil procurement price may increase by 50% in 2030 compared to the average for the past 5 years. At present, the rise in raw material prices can be passed on to most products. However, the emergence of alternative products may become a major threat even for them in the medium term. Assuming a carbon price of 140 USD/t-CO2 in 2030 as assumed by the IEA's NZE2050 Scenario, the carbon price in yen is expected to be 20,300 yen/t-CO2 when converted at the average dollar-yen exchange rate for FY2023 (1 dollar = 145 yen). If the CO2 emissions of our domestic Group companies in 2030 remain unchanged from FY2023, the carbon tax burden for that year is expected to be 144 million yen (0.8% of sales in FY2023). However, if the domestic Group company reduction plans are implemented as planned, the carbon tax burden is expected to be 113 million yen (0.6% of sales in FY2023).
Financial implications of the Physical Risk Scenario
In the Physical Risk Scenario, financial impacts associated with operation disruptions at major plants and logistics networks are expected to be significant, due to storm surges caused by large typhoons (acute risk) and sea level rise due to rising temperatures (chronic risk). In the event that a physical risk materializes, we have calculated the amount of damage to our assets and operations based on the following three scenarios: (1) the maximum damage assumed in the storm surge hazard maps published by local governments (Chiba Plant, Akoh Plant, and Ethylene Chemical CO.,LTD. flooded to approx. 3 m), (2) storm surges of with a flood depth of approx. 1 m occurring nationwide (Chiba Plant, Akoh Plant, and Ethylene Chemical CO.,LTD. flooded to approx. 1 m), and (3) storm surges of with a flood depth of approx. 1 m occurring mainly in Chiba or Hyogo Prefecture (Chiba Plant, the adjacent Ethylene Chemical CO.,LTD., or Akoh Plant flooded to approx. 1 m). In addition, a quantitative assessment of physical risks was conducted in light of the increasing possibility of storm surges due to an increase in average temperatures.
Physical Risk Simulations
| Amount of Monetary Damage | Probability | Current Monetary Damage Caused by Storm Surges (1) | Physical Risk in the Case of a 4°C Increase (2) | Incremental Increase in Physical Risk (2) - (1) | Countermeasure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total amount | Assets | Suspension of Operations | ||||||
| Scenario (1) Flooding of approximately 3 meters occurring nationwide (as predicted by hazard maps) |
7,230 million yen | 3,524 million yen | 3,706 million yen | Assumed probability: 1/1000 | 7.2 million yen annually | 14.4 million yen annually | 7.2 million yen annually | Confirming the BCP for each site and considering the necessary measures |
| Scenario (2) Flooding of approximately 1 meter occurring nationwide |
3,069 million yen | 1,752 million yen | 1,316 million yen | Assumed probability: 1/200 | 15.3 million yen annually | 30.7 million yen annually | 15.3 million yen annually | Confirming the BCP for each site and considering the necessary measures |
| Scenario (3) Flooding of approximately 1 meter occurring at Akoh or Chiba |
1,534 million yen | 876 million yen | 658 million yen | Assumed probability: 1/100 | 15.3 million yen annually | 30.7 million yen annually | 15.3 million yen annually | Confirming the BCP for each site and considering the necessary measures |
(Note)
1. The monetary amount and increase in physical risk were estimated based on
three scenarios by the Corporate Sustainability Department, the personnel in charge of promoting
carbon neutrality at the Chiba Plant, and the personnel in charge of promoting carbon neutrality at
the Akoh Plant, referring to the ideas of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and
Tourism's "A Guide to Flood Risk Assessments for Enhanced TCFD Disclosures."
2. Scenario (1) assumes that a typhoon of the same magnitude as the 1934 Muroto
typhoon (with a central pressure of 911.6 hPa at landfall) will occur nationwide. Scenario (2)
assumes that, for example, a typhoon of the same magnitude as the Ise Bay typhoon of 1959 (929 hPa)
will occur nationwide.
Scenario (3) assumes that a typhoon of the same magnitude as the Ise Bay typhoon will make
landfall in Chiba or Hyogo Prefecture.
3. Measures to address risks and opportunities
Our Group has reconsidered its response to the risks and opportunities considered to be of relatively high importance as follows.
Measures to address the Transition Risk Scenario
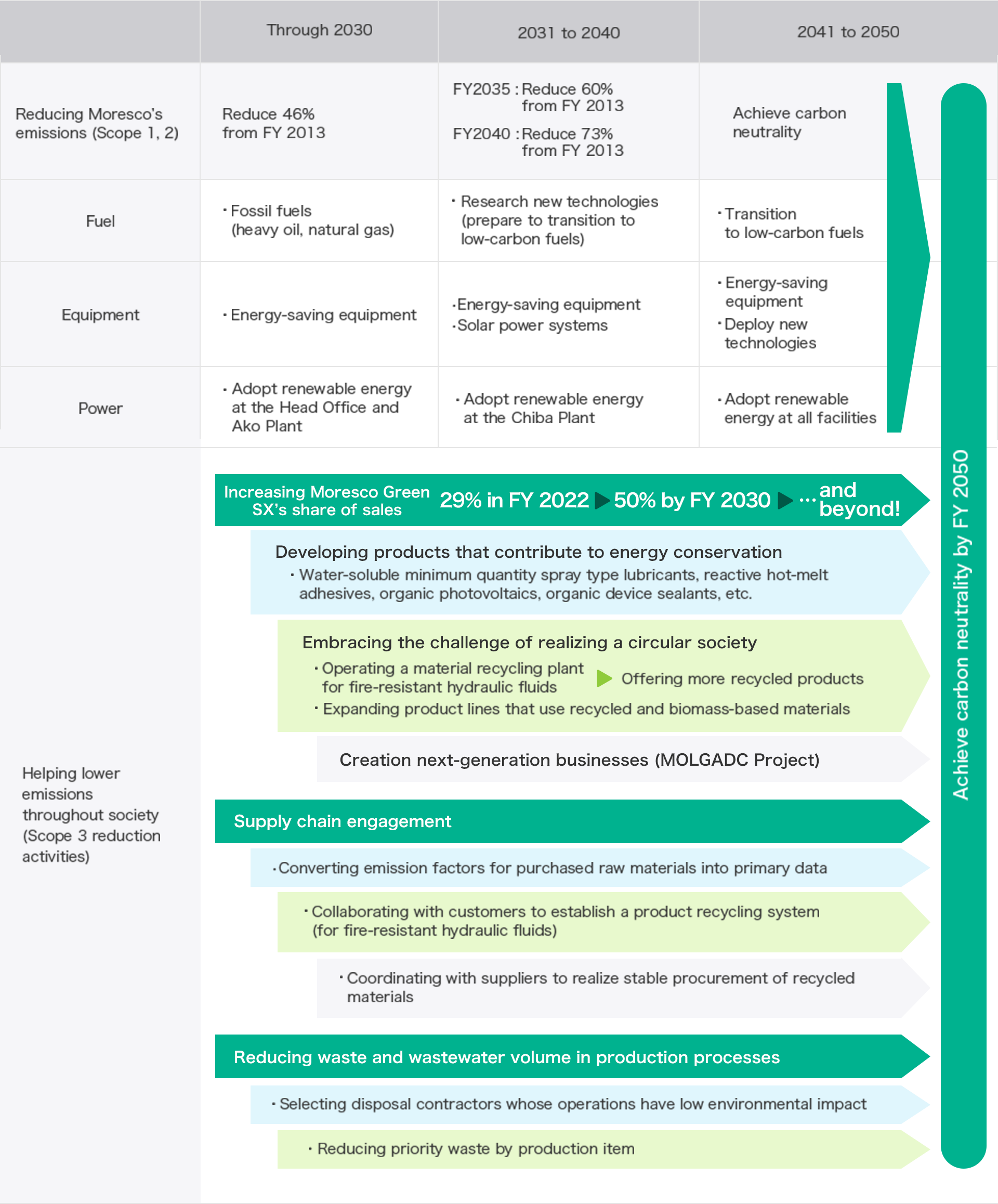
(1) Formulation of greenhouse gas reduction plans
Going forward, we will focus our efforts on
reducing greenhouse gas emissions through investments such as the introduction of renewable energy at
major sites, more efficient energy use at manufacturing sites, and the upgrading of manufacturing
facilities and air conditioning systems. The accumulated amortization for the investments required for
these activities is expected to be approximately 93 million yen.
If these measures are implemented as
scheduled and all other conditions remain constant, the Group's CO2 emissions for FY2030 are expected
to fall below the target of 5,960 tons.
(2) Selection of MORESCO Green SX products
In September 2023, our Group began certifying "MORESCO
Green SX (MGS)" products. MGS products are evaluated throughout their entire life cycles, from the
procurement of raw materials to disposal, and are certified as products that contribute significantly
to our seven materialities initiatives. With regard to certification, products proposed by each
business
department are reviewed by an internal review committee consisting of management and the heads of each
business department, and then the product is officially certified by the Sustainability Committee.
Certification and operation are then verified by a third party and evaluated for validity. In FY2024,
MGS products accounted for 34% of consolidated net sales. As part of our 10th Medium-Term Management
Plan, the Group established a plan to raise the ratio of MGS sales to 40% by FY2026 and 50% by FY2030.
(3) Development and production of polymers from non-petrochemical raw materials
As a medium- to
long-term response to climate change, we are promoting the development and production of polymers made
from non-petrochemical materials as part of the MOLGADC Project, a next-generation business creation
plan.
Measures to address the Physical Risk Scenario
As a countermeasure against natural disasters, we have already prepared a BCP for the Akoh Plant based on the assumption that a Nankai Trough earthquake could trigger a tsunami of up to 3 meters. We believe a similar scale of damage and countermeasures will be necessary for storm surges and increasing sea levels. The Chiba Plant is expected to suffer similar damage. Based on the estimated physical risks associated with climate change, we will review our BCP for natural disasters at our major sites and consider necessary measures.
Ⅲ. Risk Management
Our Group established the Compliance and Risk Management Committee and the Sustainability Committee to address various risks inherent in and related to management issues, and we are working to enhance risk management. In principle, the Sustainability Committee meets on the same day and with the same participants as the Compliance and Risk Management Committee. We have developed a system to examine sustainability-related risks and opportunities within a wide range of management risks.
With regard to risks and opportunities related to sustainability issues, the Sustainability Committee
has identified seven important issues (materiality) based on interviews with internal and external
stakeholders and discussions with Business Divisions and related departments. We recognize that
"reducing environmental impact (including climate change)" is one of the most important materiality
items related to our business activities. When it comes to risks and opportunities related to climate
change, the Corporate Sustainability Department plays a central role in conducting study sessions at
each Business Division and the Life Science R&D Department based on respective awareness surveys and
identifying important risks and opportunities. The identified risks and opportunities are then reported
to the Sustainability Committee to deliberate and form response policies, measures, and targets
accordingly. The contents of the deliberations are reported to the Board of Directors and final
decisions will be made under their supervision.
In addition, risks related to management strategies and
other management decisions are analyzed and discussed by relevant departments after receiving advice
from external experts as necessary.
*Details of the Group's Materiality and the Process of Identifying Them
Ⅳ. Metrics and Targets
1. Indicators and targets for assessing climate-related risks and opportunities
The Group has identified "achieving the reduction of environmental impact" as one of its seven materiality items. As one of the specific initiatives, we are promoting the "reduction of CO2 emissions, waste materials, and wastewater from the production processes". Regarding greenhouse gas emissions, another important risk related to environmental impact, we are promoting quantitative measurements and target setting of below categories based on the standards of the GHG Protocol: (1) direct emissions from the use of heavy oil, gas, and other fuels in our manufacturing processes and business activities (Scope 1), (2) indirect emissions from the purchase of electricity and heat energy from other companies (Scope 2), (3) indirect emissions other than those defined in Scope 1 and Scope 2 (emissions from the supply chains related to the Group's activities)
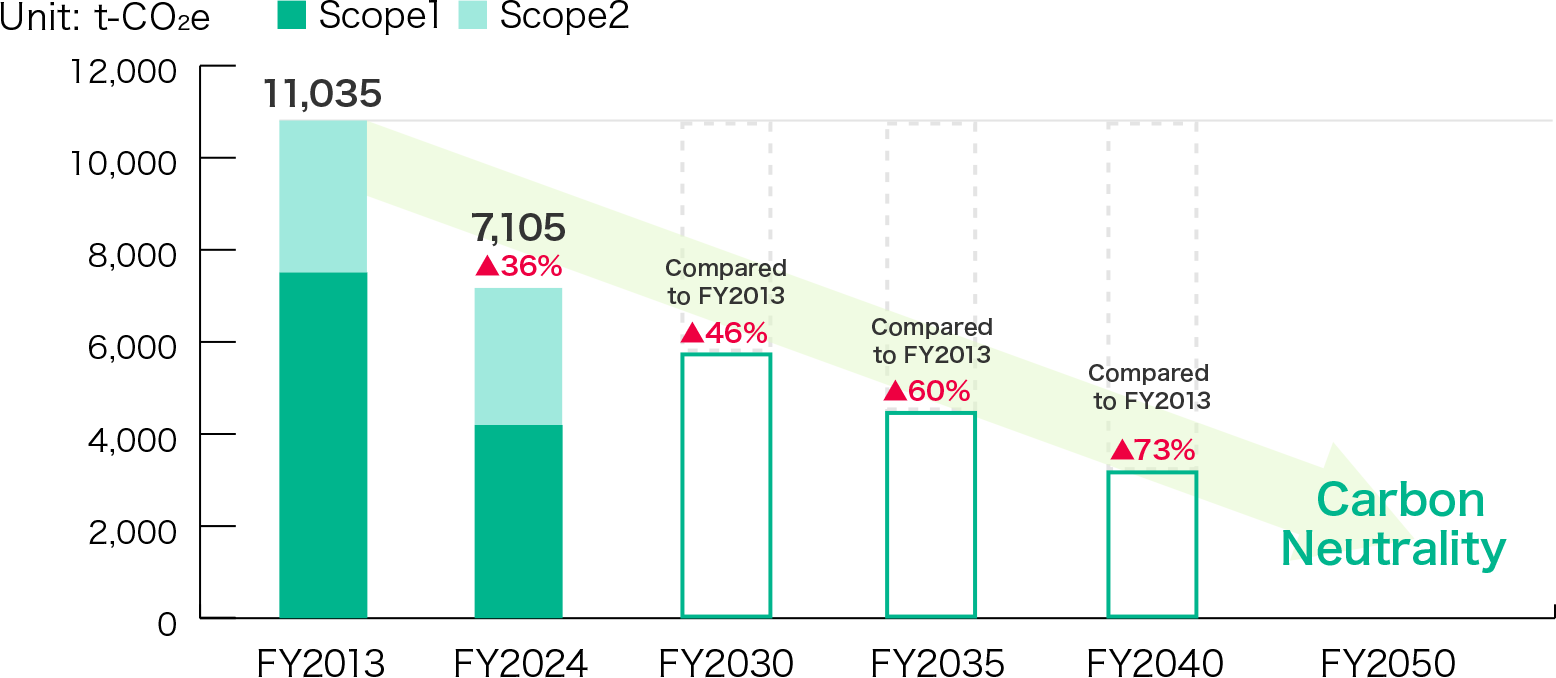
2. Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction Targets and Results
(1) Reduction targets
We have set a target of 46% reduction in total greenhouse gas emissions
under Scope 1 and Scope 2 (compared to FY2013) by the end of FY2030, (Target 1) and are aiming for
carbon neutrality including Scope 3 by FY2050 (Target 2).
(2) Results
For FY2023, our actual greenhouse gas emissions (total for Scopes 1 and 2) were 7,104
t-CO2e. Compared to the baseline figure of 11,035 t-CO2e in FY2013, we achieved a reduction of 36% by
FY2023 through measures such as improving the efficiency of energy use and thorough repair and
maintenance of energy-related equipment.
(GHG Emissions Results)
Roadmap to Carbon Neutrality
| Target | Boundary | Target Fiscal Year | Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Goal 1 |
Scope 1+2 emissions |
MORESCO domestic group companies (consolidated) |
FY2030 |
46% reduction (compared to FY2013) |
Goal 2 |
Scope 1+2 emissions |
MORESCO domestic group companies (consolidated) |
FY2050 |
Carbon neutral |